Confined Catalysis
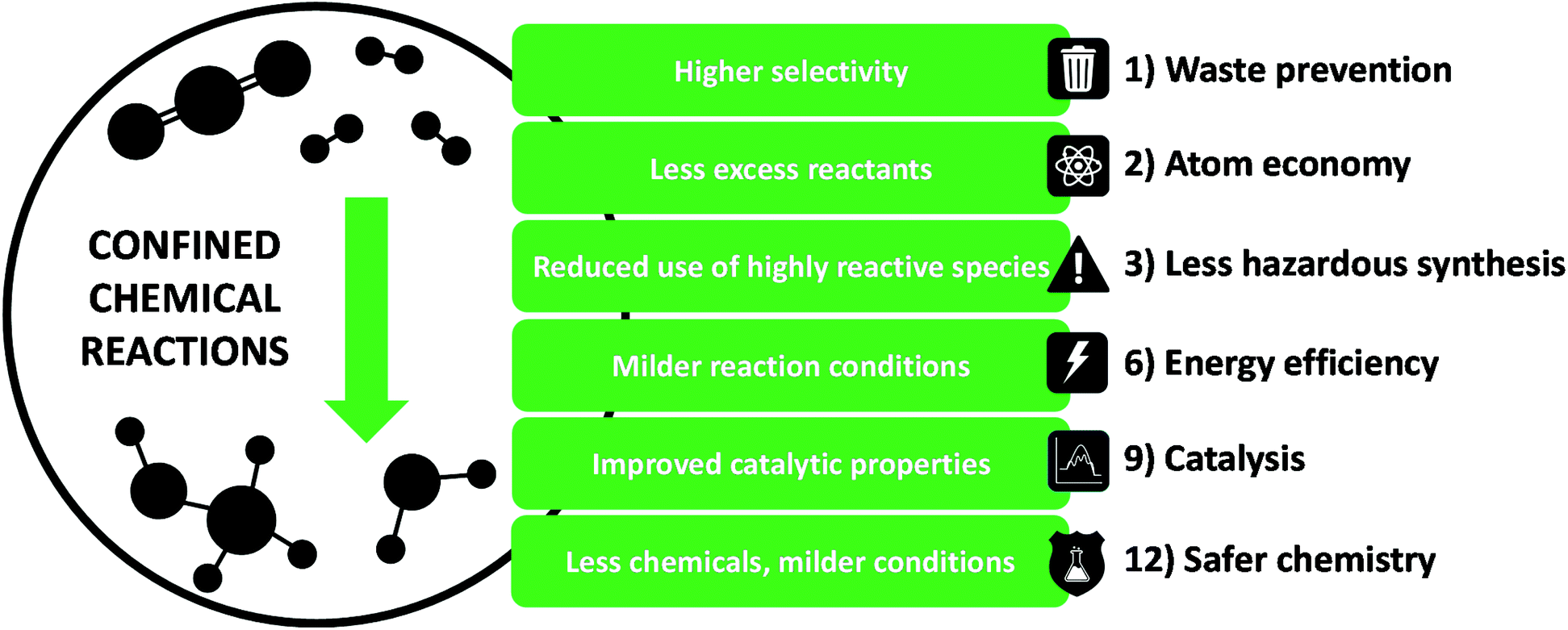
Chemical reactions happening in spatially restricted nanospaces can present unique chemical and physical behaviours. When the dimensions of the reaction space are in the same order of magnitude as the diameters of molecules, they can experience for instance slower diffusion rates, local concentration or pressure build ups. Those effects can dramatically change the course the catalytic reactions. Restricted spaces can also stabilize unlikely intermediates by wall interactions of even avoid the formation of bulky intermediates, interfering in reaction pathways. All this power can be harvested to make chemical reactions more selective and in milder conditions, which is what we have demonstrated in a review article in which we linked confined catalysis to the principles of Green Chemistry (Terra, Green Chem., 2022).
We have demonstrated that mesoporous silica can concentrate and stabilize Cu (I) species inside its pores and perform the A3-coupling reaction at ppm levels of catalyst (Terra, ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2019), and more work on this field is yet to come…